Introduction
In this article, we will cover in detail for planning and operational variances for materials. We have covered the direct material price variance in previous article. However, in this article, we will go further to planning and operational variances for direct material price as well as planning and operational variances for direct material usage.
Direct materials form the largest chunk of the product cost. Careful planning for material usage and securing favorable prices, can save costs and increase profitability. Total material costs can change due to a change in raw material pricing or change in component usage. Analysis of changes in planned and revised budgets for materials is called material variance.
Definition
Material variance can be defined as:
“The difference between the standard cost of material and the actual cost of material is called material variance”.
Material variance can be divided into the material price and material usage variances. A material price variance is simply finding each unit of product cost in comparison to the estimated cost. Material usage variance deals with the total input material component(s) usage per unit of product. Both material price and usage variance can be analyzed in terms of planning and operating variances.
Material price and material usage variances can be calculated similarly to the labor rate variances. The general formulae to calculate the material variances are as below:
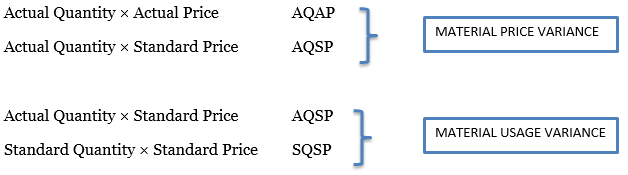
Simplified Formula:
Material price Variance = AQ × (AP – SP)
Material usage Variance = SP × (AQ – SQ)
Working Example
We will use the same example which we have covered in the previous article on planning and operational variance for labor as follow:
Green star produces agriculture fertilizers with following information provided.
The company management analyzed past data and set the budgeted rates as following:
Standard hours per unit of product = 1.1
Standard direct labor rate per hour = $ 8.50
Standard usage of material per unit = 1.2 kg per unit
Standard price of material per kg = $ 70
Standard price of material per unit = $84 per kg
During production times, the management REVISED the budgets with updated information as:
Revised price of material per kg = $ 71
Revised labor rate per hour = $ 8.75 per hour
Revised hours per unit of product = 1.05
Revised usage of material per unit = 1.175 kg per unit
Revised usage of material per unit = $83.425 per kg
After the production period the company recorded following actual results:
Actual Production = 15,400 Raw Material usage = 16,555 KGs
Actual cost of raw material = $ 1,191,960
Actual labor costs= 16,632 hours and $ 143,035 or $ 8.5998 per hour or round down to $8.60 per hour
Solution:
We’ll calculate the material operational and planning variances.
Direct Material Price Operating Variance:
Actual cost – (actual usage × Actual price) = $ 1,191,960 – (16,555 × 71)
Material price operating variance = $ (16,555) ADVERSE
Alternatively, we can calculate the material price operational variance by using the format below:
| US$ | |
| 16,555 kg of material should cost (revised standard) (×71) | 1,175,405 |
| They did cost | 1,191,960 |
| Direct Material Price Operational Variance | (16,555) ADVERSE |
Direct Material Price Planning Variance:
(Revised Price – Standard Price) × Actual Material Usage = (71 -70) × 16,555
Material Price Planning Variance = $ (16,555) ADVERSE
Alternatively, we can calculate the direct material price planning variance by using the format below:
| US$ per Kg | |
| Original Standard Price | 70 |
| Revised Standard Price | 71 |
| Direct Material Price Planning Variance per kg | (1) ADVERSE |
| Actual Quantity of materials used | 16,555 kg |
| Direct Material Price Planning Variance in US$ | (US$16,555) ADVERSE |
The sum between direct material price planning and operational variance is as follow:
Planning Price Variance (US$16,555) ADVERSE
Operational Price Variance (US$16,555) ADVERSE
Total Material Price Variance (US$33,110) ADVERSE
We can reconcile the one off calculation of the direct material price variance as follow:
The direct material price variance is calculated as follow:
From the formula above, we can simplify the formulas as follow:
Direct Material Price Variance = Actual Cost – AQSP
= 1,191960 – (16,555 × 70)
= US$33,110 ADVERSE
Direct Material Usage Operating Variance:
(Actual Quantity – Revised Quantity) × Original Standard Price = (16,555 – 18,095) × 70
Material Usage Operating Variance = $ 107,800 FAVORABLE
Alternatively, we can calculate the direct material usage operational variance as per the format below:
| Kg | |
| 15,400 units of material should use (×1.175 kg) | 18,095 |
| They did use | 16,555 |
| Direct Material Usage Operating Variance in kg | 1,540 FAVORABLE |
| Original Standard Price per Kg of materials | US$70 |
| Direct Material Usage Operational Variance in US$ | US$107,800 FAVORABLE |
Direct Material Usage Planning Variance:
(Revised material usage – standard material usage) × Standard Price = (18,095 – 18,480) × 70
Material Usage Planning Variance = $ 26,950 FAVORABLE
Alternatively, we can calculate the direct material usage planning variance as per the format below:
| Kg | |
| 15,400 units should use (original standard) (×1.2 kg) | 18,480 |
| 15,400 unit should use (revised standard) (×1.175 kg) | 18,095 |
| Direct Material Usage Planning Variance in kg | 385 FAVORABLE |
| Original standard price per kg of material | US$70 |
| Direct Material Usage Planning Variance in US$ | US$26,950 FAVORABLE |
The sum between direct material usage planning and operational variances are as follow:
Planning Usage Variance US$26,950 FAVORABLE
Operational Usage Variance US$107,800 FAVORABLE
Total Material Usage Variance US$134,750 FAVORABLE
We can reconcile the one off calculation of the direct material usage variance as follow:
The direct material usage variance is calculated as follow:
Direct Material Usage Variance = AQSP – SQSP or SP × (AQ – SQ)
= 70 × [16,555 – (15,400×1.2)]
= US$134,750 FAVORABLE
In addition, we can also calculate the direct material variances in total as follow:
| Total Variances | US$ |
| 15,400 units of material at original standard costs (×84) | 1,293,600 |
| Actual material costs | 1,191,960 |
| Total Variances | 101,640 FAVORABLE |
The sum of all the variances calculated above shall equal to the direct material variances in total.
We can combine the results for material operating and planning variances as:
| Variances | $ Favorable | $ Adverse |
| Planning Variances | ||
| Direct Material Price Planning Variance | (16,555) | |
| Direct Material Usage Planning Variance | 26,950 | |
| NET: | 10,395 | |
| Operating Variance | ||
| Direct Material Price Operational Variance | (16,555) | |
| Direct Material Usage Operational Variance | 107,800 | |
| NET: | 91,245 | |
| Total Variance: | $ 101,640 F |
Both material price and usage variance can occur due to several reasons.
| Variance | FAVORABLE | ADVERSE |
| Material PRICE | Discount on bulk purchase Low quality material components Inaccurate budgeting Change of supplier Change of product formula | Higher input component prices Inaccurate budgeting Change of Supplier High quality input components |
| Material USAGE | Efficient use of raw material Inaccurate budgeting Skilled and motivated staff Usage of new production machinery | Lower skilled Staff Inaccurate budgeting Old production machinery |
Analysis and Interpretation
Inefficiencies in production processes Material usages waste. Some of the material can occur due to testing, scrapping, remodeling, and evaporating processes. Testing, remodeling and evaporating types of material wastes can be included in pre-planned budgets or the revised material quantity budgets.
Material Price Planning Variance:
Material price planning involves analyzing historic material prices, inflation adjustments, and supplier relations. Many products require several input components; a fraction of price discounts in each component can yield large material price variance. The most important factor in material price planning is to consider the material quality and price balance. Often lower prices result in low quality raw materials that in turn will result in the cheap quality final product and a loss in sales. Reliable suppliers with long-term contracts can provide high quality materials at reasonable prices.
Material Price Operating Variance:
It’s inevitable to see any deviations in the planned and actual budgets. Similarly, material prices may change during the production process, causing a variance in material prices. An in-depth analysis of material price operating variance can identify whether the variance is caused due to a hike in prices or usage problems. Once the management revises the original budgets to follow any material price changes, it then becomes the responsibility of operations managers to achieve those revised targets. Any gaps in revised and actual material price budgets can then be used for the next budget planning and forecast.
Material Usage Planning Variance:
Material usage planning starts with identifying the product formula. Careful planning for all input components in a product can save discrepancies in material usage later. The management can also plan for high profit yielding products in a product mix for the best utilization of production resources. Production machinery, labor skill level, and controls play an important role in achieving material usage efficiency. Material wastage can also occur naturally with testing, evaporating, and scrapping processes. These recurring or predictable material usage changes should be adjusted in the planning phase or the revised budgets during the production period.
Material Usage Operating Variance:
Inefficient production operations cause material wastage. Old machinery, non-skilled labor, and lose controls may also lead to material usage operating variances. Most of the operating measures for material usage are controllable factors. Some uncontrollable factors such as remodeling in product, or change in product formula may also cause material usage operating variances. However, production managers should only be held accountable for operating material variances.
Benefits and Limitations
Total material variance can occur due to a change in price and usage of input materials. A change in production costs directly affects the contribution or operating profit margins. Competitive markets demand for responsive actions to adjust to the market trends. A careful interpretation of material variance can help management identify the reasoning for change in variance. It can help management to compare supplier relations and prices.
Study of material variance also encourages operational managers and labor to achieve efficiency in production processes. If performance and rewards for operational staff are linked with material efficiencies it often temps them to manipulate the material usage. Operational managers may also argue on the material prices if their performance in appraised based on material variances.

