Introduction
In this article, we will cover in detail of the planning and operational variances for labor. This includes the further breakdown into direct labor rate operational variance, direct labor rate planning variance, direct labor efficiency operational variance and finally direct labor efficiency planning variance.
In this article, we will illustrate the detail breakdown of both direct labor rate variance and direct labor efficiency variance into planning and operational variances. Before going further, let’s go through the overview and key concepts of the labor variances.
Labor variance is unique in the sense that labor hours cannot be procured or saved in advance as materials. Top management can only plan using past data and forecasts to set standard labor hour rates and total labor costs. During operations, many factors affect production, and results are often different from planned. The planning and operational variances for any measure can be calculated as the difference between planned budget and revised and actual results and revised budgets.
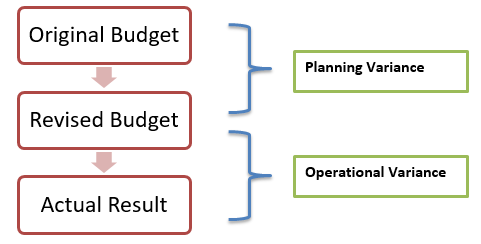
Total direct labor variance can also be divided into direct labor rate and direct labor efficiency variances.
Total Direct Labor Variance = Direct Labor Efficiency Variance + Direct Labor Rate Variance
For planning and operational point of view, each of the two components can then be analyzed as Direct Labor Rate Planning and Operational Variance and Direct Labor Efficiency Planning and Operational efficiency.
Formula to Calculate Labor Variances
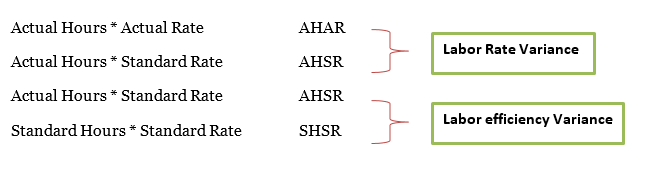
We will cover all formula related the labor variances. This includes the labor rate variance (both planning and operational variances) and labor efficiency variance (both planning and operational variances.
Working Example
Green star produces agriculture fertilizers with following information provided.
The company management analyzed past data and set the budgeted rates as following:
Standard hours per unit of product = 1.1
Standard direct labor rate per hour = $ 8.50
Standard usage of material per unit = 1.2 kg per unit
Standard price of material per unit = $ 70
During production times, the management REVISED the budgets with updated information as:
Revised price of material per unit = $ 71
Revised labor rate per hour = $ 8.75 per hour
Revised hours per unit of product = 1.05
Revised usage of material per unit = 1.175 kg per unit
After the production period the company recorded following actual results:
Actual Production = 15,400 Raw Material usage = 16,555 KGs
Actual cost of raw material = $ 1,191,960
Actual labor costs= 16,632 hours and $ 143,035 or $ 8.5998 per hour or round down to $8.60 per hour
We’ll calculate the Direct Labor Planning and Operational Variances as follow:
Operational Variance for Labor Rate:
Direct labor rate operational variance = (Revised Rate – Actual Rate) × Actual Hours
Direct labor rate operational variance = (8.75 – 8.5998) × 16,632 = US$2,495 FAVORABLE
Alternatively, we can calculate the direct labor rate operational variance as per the format as follow:
| US$ | |
| 16,632 hours should cost at revised standard rate (8.75) | 145,530 |
| They did cost at | 143,035 |
| Direct Labor Rate Operational Variance | 2,495 FAVORABLE |
Planning Variance for Labor Rate:
Direct labor rate Planning variance = (Revised Rate – Standard Rate) × Actual Hours
Hence, the Direct labor rate Planning variance = (8.75 – 8.50) × 16,632
Direct labor rate Planning variance = 0.25 × 16,632 = (US$4,158) ADVERSE
| US$ per Hour | |
| Original Standard Rate | 8.50 |
| Revised Standard Rate | 8.75 |
| Direct Labor Rate Operational Variance per hour | (0.25) ADVERSE |
| Actual number of hours worked | 16,632 |
| Direct Labor Rate Operational Variance in US$ | (US$4,158) ADVERSE |
The sum between direct labor rate planning and operational variances are as follow:
Planning Rate Variance (US$4,158) ADVERSE
Operational Rate Variance US$2,495 FAVORABLE
Total Rate Variance (US$1,663) ADVERSE
We can reconcile the one off calculation of the direct labor rate variance as follow:
The direct labor rate variance is calculated as follow:
From the formula above, we can simplify the formulas as follow:
Direct Labor Rate Variance = AH × (AR – SR)
= 16,632 × (8.60 – 8.50)
= US$1,663 ADVERSE
Operational Variance for Labor Efficiency:
Direct Labor Efficiency Operational Variance = (Actual Hours – Revised Hours) × Standard Rate
Direct Labor Efficiency Operational Variance = (16,632 – 16,170) × 8.50 = US$3,927 ADVERSE
Alternatively, we can calculate the direct labor efficiency operational variance as per the format follow:
| Hours | |
| 15,400 units of product should take (×1.05) | 16,170 |
| They did take | 16,632 |
| Direct Labor Efficiency Operational Variance in hour | (462) ADVERSE |
| Original Standard Rate per hour | 8.50 |
| Direct Labor Efficiency Operational Variance in US$ | (US$3,927) ADVERSE |
Planning Variance for Labor Efficiency:
Direct labor efficiency planning variance = (Revised Hours – Standard Hours) × Standard Rate
Direct labor efficiency planning variance = (16,170 – 16,940) × 8.50 = $ 6,545 F
Alternatively, we can calculate the direct labor efficiency planning variance as follow:
| Hours | |
| 15,400 units should take at original standard rate (× 1.1) | 16,940 |
| 15,400 units should take at revised standard rate (×1.05) | 16,170 |
| Direct Labor Efficiency Planning Variance in hours | 770 FAVORABLE |
| Original Standard Rate per hour | 8.50 |
| Direct Labor Efficiency Planning Variance in US$ | US$6,545 FAVORABLE |
The sum between direct labor efficiency planning and operational variance is as follow:
Planning Efficiency Variance US$6,545 FAVROABLE
Operational Efficiency Variance (US$3,927) ADVERSE
Total Efficiency Variance US$2,618 FAVORABLE
We can reconcile the one off calculation of the direct labor efficiency variance as follow:
The direct labor efficiency variance is calculated as follow:
Direct Labor Efficiency Variance = AHSR – SHSR or (AH – SH) × SR
= (16,632 – (15,400×1.1) × 8.50
= US$2,618 FAVORABLE
In addition, we can also calculate the direct labor variance in total as follow:
| Direct Labor Variance in total | US$ |
| 15,400 units at original standard (1.1×8.5) | 143,990 |
| Actual Labor Cost | 143,035 |
| Total Direct Labor Variance | 955 FAVORABLE |
The sum of all the variances calculated above shall equal to the direct labor variance in total.
We can also summarize the variance according to planning and operational categories and reconcile to the direct labor variance in total as below:
| Variances | $ Favorable | $ Adverse |
| Planning Variances | ||
| Direct Labor Rate Planning Variance | (4,158) | |
| Direct Labor Efficiency Planning Variance | 6,545 | |
| NET: | 2,387 | |
| Operational Variances | ||
| Direct Labor Rate Operational Variance | 2,495 | |
| Direct Labor Efficiency Operational Variance | (3,927) | |
| NET: | (1,432) | |
| Total Variances: | $ 955 F |
Labor rate and efficiency variance causes can be summarized as:
| Variances | FAVORABLE | ADVERSE |
| LABOR RATE | Lower skilled Staff Inaccurate budgeting Lower staff motivation Labor idle time | Higher skilled Staff Inaccurate budgeting Sudden change in labor rate Labor idle time |
| LABOR EFFICIENCY | Higher skilled Staff Inaccurate budgeting Higher staff motivation | Lower skilled Staff Inaccurate budgeting Lower staff motivation |
Note the link between causes in labor rate and efficiency variances; practically it often happens a favorable variance in measure causes an adverse variance in other.
Analysis and Interpretation
Direct Labor Rate Variance is simply the judgment for the labor cost between planned and actual results. Direct Labor efficiency is the analysis for labor hour per unit production. Both labor rate and efficiency variances can also be examined with planning and operational parameters.
Direct Labor Rate Planning Variance
The management pre-plans for the labor hours required per unit in production. However, it is likely that labor hours will deviate for several reasons. Responsive and efficient management will then revise the labor hour budgets. Labor rate planning variance is simply the deviation between original estimates and revised budgets for the labor hours. i.e. the planned and revised labor rate per hour
Direct Labor Rate Operational Variance
During operations, labor hours may change. Sometimes due to idle hours or efficient labor management that can decrease the total labor hours. The shortage of regular labor staff or temporary hiring of skilled labor due to expansion requirements can also cause a change in the total labor hours. At the end of each production unit, the management will then account for the actual labor hours against the revised labor hours. Any deviation will be noted as labor rate operational variance as the production operations caused the variance.
Direct Labor Efficiency Planning Variance
Labor efficiency is directly linked with the labor skill levels. Ongoing and stable production staff and labor can be assessed for their skill level based on historic outputs. The management can plan accordingly for the labor hours taken to produce each product unit. If the skilled labor takes less hours to produce more (or even same) number of units, the production will record a favorable labor efficiency planning variance.
Direct Labor Efficiency Operational Variance
Depending on the production demands to increase or decrease the labor staff, the management will likely revise the original budgets. The focus then shifts to achieve the revised labor hour targets. Any differences in revised budgets and the actual results due to efficiency in labor staff is recorded as labor efficiency operational variance.
Responsibility of Labor Variance
Total labor variance arising from labor rate and efficiency depends on the pre-planning and operations. Generally, labor requirements are well known in advance for stable organizations, so labor planning variance is less likely to occur. Project specific and skilled labor procurement is necessarily the responsibility of human resource departments. However, production managers are responsible for the production efficiency of skilled labor.
Advantages of Labor Variance Analysis
Any business management cannot procure and store in advance for labor skills. Changing business environments calls for quick and responsive approaches in operations too. Total labor variance depends on the labor rates and efficient use. Sudden labor rate change such as due to a change in national wage rate policy cannot be controlled by the management.
However, skilled labor efficiency can be improved with enhances training and reducing idle labor hours. Rarely idle labor hours can also be due to uncontrollable factors such as shortage of raw material or interruption in energy supplies. Breakdown of labor variance into planning and operational sections offers a realistic approach for results evaluation. Identification of causes for labor variance can help management with better budget planning and forecasting. It also helps management with the best utilization of skilled labor hours.
