Introduction
Accounting for borrowing costs are crucial; especially when an entity has a large project to build and need source of fund from bank. When we borrow any fund from bank, the bank usually charges the interest which we commonly call it as finance costs as well as other charges associated with such borrowing. We can capitalize the borrowing costs in order to arrive at the value of an asset. So what is the borrowing costs? How can we deal with the accounting for borrowing costs ?
Relevant IAS for the Accounting for Borrowing Costs
The accounting standard that is applicable for the accounting of borrowing costs is IAS 23 – Borrowing Costs. Thus, in the sections below, we will cover the relevant definition, scope, recognition, practical examples as well as the dislosures’ requirement.
Before we show how to account for borrowing costs and present in the financial statements, let’s understand some key definitions that relate with IAS 23 – Borrowing Costs.
Definition
IAS 23 – Borrowing Costs defines the borrowing costs as follow:
“Borrowing costs are interest and other costs that an entity incurs in connection with the borrowing of funds”.
In addition to the word borrowing costs, there is another word that we commonly see in this standards. It is Qualifying Assets. So what is qualify asset?
Qualifying assets are those assets that are necessary to take a substantial period of time in or der to get ready for its used or sale.
In some circumstances, the qualifying assets may include any assets as follow:
- Inventories
- Manufacturing plants
- Intangible assets
- Power generation facilities
- Investment properties
Practically, any inventories or financial assets that take a short period of time to be available for use or sales are not considered as qualifying assets. Additionally, we would not consider as qualify asset if such assets are ready for any intended use at the time of purchase of acquire.
As per IAS 23, the borrowing costs may include items as follow:
- Interest expense that incurred as result of such borrowing. We shall calculate this interest by using the effective interest method in accordance with IAS 39 Financial Instruments Recognition and Measurement;
- Any bank charges or finance charges in respect of finance leases that an entity recognize in accordance with IAS 17 Lease (Further replaced by IFRS 16 – Lease);
- We can also consider as an adjustment to interest costs for any exchange differences that arise from the borrowing in foreign currency.
Scope
In accordance with IAS 23, the standard shall be applied for each entity that are qualified for. Please note that IAS 23 does not deal with any actual or imputed cost of equity. In addition, IAS 23 does not require to apply this standard for the the following assets resulting from the acquisition, construction or production:
- Any qualifying asset that an entity measures at fair value, for instance a biological asset; or
- Inventories that an entity manufactures or produces in large quantities and on a repetitive basis.
Recognition
In accordance with IAS 23, any company or entity shall capitalize borrowing costs on a qualifying assets as part of the assets where such borrowing costs are directly attributable to the acquisition, construction or production of such assets. Such entity shall only capitalize those borrowing costs as part of the asset value if and only if it is probable that such assets will generate future economic benefit to the entity and such costs are able to be measure reliably. Otherwise, those entities shall recognize such costs as expense for that relevant period it incurs.
If the specific or intended purpose of borrowing the fund is just to obtain a qualifying asset, such amount of borrowing costs eligible for capitalization shall be determined as the actual costs that incurred for that borrowing during the period less any revenue resulting from the investment or investment income on the temporary investment of such borrowings.
Finally, the entity shall determine the amount of borrowing costs that are eligible for capitalization by applying the capitalization rate to the expenditures on that asset if such borrowing is for generally uses for the purpose of obtaining a qualify asset. IAS 23 also specifically mentions that the capitalization rate shall be the weighted average of the borrowings that are applicable to the borrowings of the entity and these borrowings are outstanding during the period. Such borrowings shall not be the borrowings that are specifically for the purpose of obtaining a qualify asset. In addition, the amount of borrowing costs capitalized during a period shall not exceed the amount of borrowing cost that incurs during that period.
Practical Examples
In order to illustrate how we can account for borrowing costs correctly, let’s go through two example below. The first example will cover the borrowing specifically intended for qualify asset while the second example will cover the borrowing for general purpose of the qualify asset.
Example 1:
On 1 January 2018 ABC Co borrowed $1.5m to finance the production of two assets. ABC Co expects these two assets to take a year to build. The work has started during 2018. ABC Co has drown down the loan facility from one commercial bank on 1 January 2018, and the company will utilize it as follows, with the remaining funds has been invested temporarily.

Calculate the borrowing costs that ABC Co can capitalize for each of the assets. Then calculate the costs of the two assets as at 31 December 20X6. Ignoring compound interest.
Solution:
In the above example, the borrowing is specifically for the qualifying asset. Thus the amount of borrowing costs available for capitalization would be the actual borrowing costs incurred on those borrowings during the period, less any investment income on the temporary investment of those borrowings. Below is the working calculation of the borrowing costs that ABC Co need to record in the Balance Sheet.
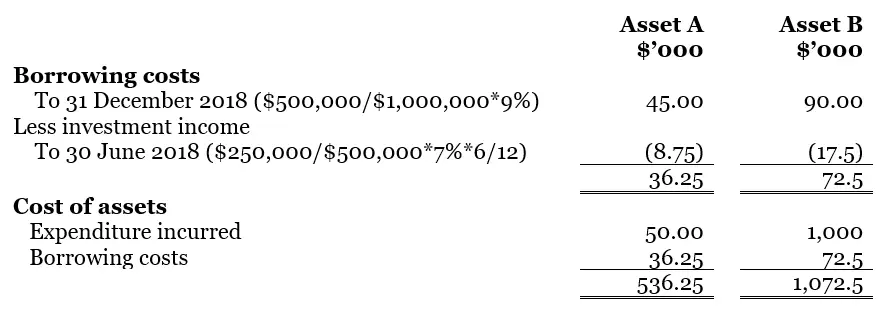
Thus, from the above calculation, the total borrowing costs are US$36,250 and US$72,500 for asset A and asset B respectively. Thus, the total costs of assets would be US$536,250 and US$1,072,500 respectively for asset A and B. ABC Co shall need to record and present such borrowing costs inclusively as the costs of those two assets in the Balance Sheet under the Non-Current Assets section.
Then ABC Co shall account for depreciation and recognize such depreciation expense the same way as other fixed assets.
Example 2:
Suppose further that ABC Co had three types of loan or payable in place at the beginning and end of financial year 2018 as follow:

The rate to fund the construction of a qualify asset (a piece of mining equipment) is at 8.9% debenture. This construction began on 01 July 2018.
ABC Co began the construction of a qualifying asset, a piece of machinery for a hydroelectric plant, using existing borrowings, on 1 January 2018. ABC has incurred the expenditure in which such expenditure was drawn down for the construction at $20m on 01 January 2018, $15m on 01 October 2018.
Determine the borrowing costs that ABC Co can capitalize for the hydro-electric plant machine.
Solution:
In this example, the borrowing were obtained generally for qualify asset. Thus, the amount of borrowing costs eligible for the capitalization is the amount that come from applying the capitalization rate which is the weighted average rate of the loans to the expenditure incurred for that qualify asset.
Therefore, the capitalization rate is calculated as follow:
Weighted average rate = 10%*[100/ (100+50)] + 9.5%*[50/ (100+50)]
= 0.06 + 0.03 = 9%
The capitalization rate equal to the weighted average rate which is at 9%.
Thus the borrowing costs will be calculated as follow:
Borrowing costs = US$20m*9% + US$15m*9%*3/12
= US$1.8m + US$0.33m
= US$2.13m
Therefore, the total borrowing costs of US$2.13m shall be capitalized into the asset value.
Disclosures’ requirements
In accordance with IAS 23 – Borrowing Costs, an entity shall disclose any borrowing costs incurred for qualify asset as follow:
- Shall disclose the amount of borrowing costs that such entity capitalized during the period being reported;
- Shall disclose the capitalization rate that such entity used in order to determine or calculate the amount of borrowing costs eligible for capitalization.

