Introduction
Basically, when we are talking about types of financial statements, we will firstly think about Income Statement, Balance Sheet, Statement of Changes in Equity as well as the Cash Flow Statements. Financial statements are basically arising from the the summary of business transactions as result of business activities during the course of day today business operation. Normally, all kinds of stakeholders need such Financial statements in order to make any business decision; especially on any investment opportunities or seeking any financing facilities .
What are difference types of financial statements?
Each types of financial statements provides users with different financial information. In this section, we will discuss more detail about the differences of the four types of the financial statements.
Income Statements
We commonly call income statement because this statement summary the different types of business revenue both the turnover from ordinary business activities as well as other types of incomes and expenses incurred during the course of business activities. Income Statement is also known as statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income. In practice, the income statement is commonly presented as below:
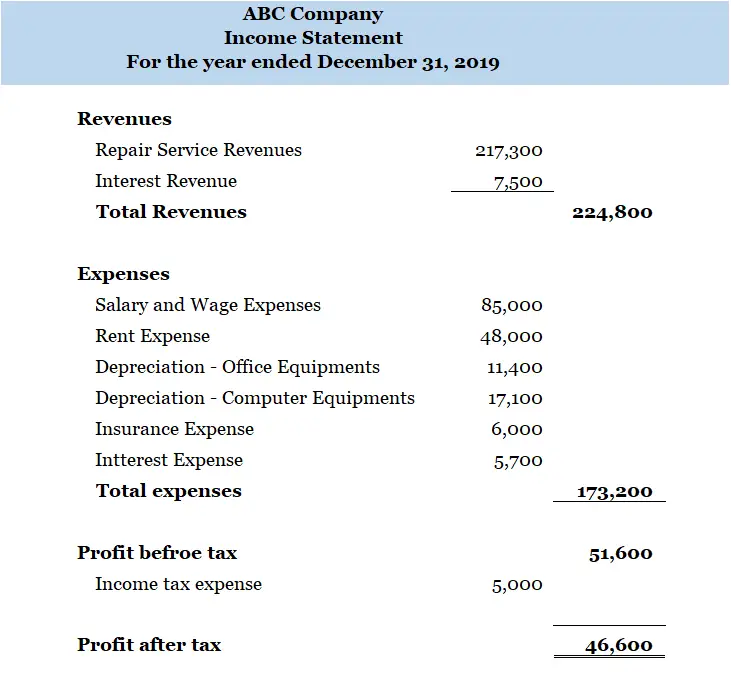
Balance Sheet or Statement of Financial Position
Balance Sheet is one of the elements of the financial statements. It summaries all the assets, liabilities and equity of an entity. The assets section consists of both current assets and non-current assets.
Current assets are assets that an entity own or control and can generate future economic benefit flow to that entity. Below are the example of current assets:
- Cash and Cash Equivalents
- Account Receivable
- Prepaid Rent
- Prepaid Insurances
- Other currents assets
Non-current assets are assets that have useful life more than one year. It consists of:
- Land
- Building
- Office Equipment
- Computer Equipment
- Intangible assets
- Other non-currents assets.
Commonly, we call land, building, office equipment, computer equipment and other non-current assets with similar nature as Property Plant and Equipment (PPE).
The same for liabilities section, it consists of current liabilities and non-current liabilities. Current liabilities are those that are expected to pay within twelve months while non-current liabilities are those that an entity is expected to pay more than one year.
In equity section, it consists of share capital, retained earnings as well as other reserves
Below is the simple Balance Sheet in practice:
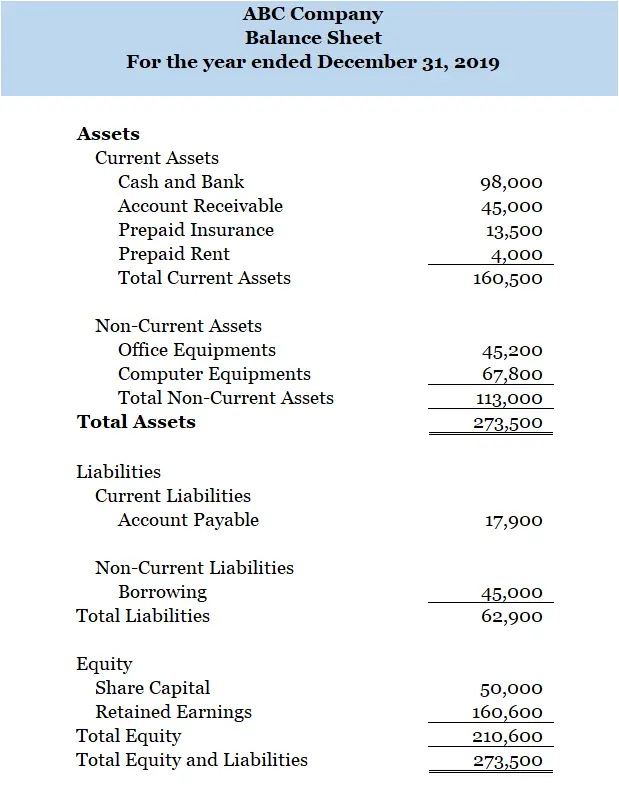
Statement of Changes in Equity
Statement of changes in equity shows the movement of share capital, retained earnings as well as other reserves over a period of time. When there is an additional capital injection, the share capital will increase. Retained earnings is a accumulation of the profit or loss of an entity from one accounting period to another. While other reserves may consist of for example the currency translation reserve.
Below is the example of statement of changes in equity in practice:
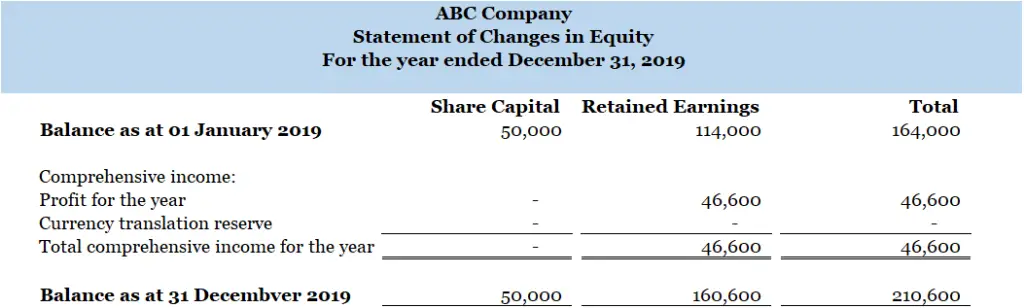
Cash Flow Statement
Statement of cash flow indicates the movement of cash and cash equivalents over a period of time. It shows movement of both cash receipt and cash payments. Cash flow of a business normally come from three different activities. Those are cash flow from operating activities, cash flow from investing activities and cash flow from financing activities. Below is the basic sample of cash flow statement:
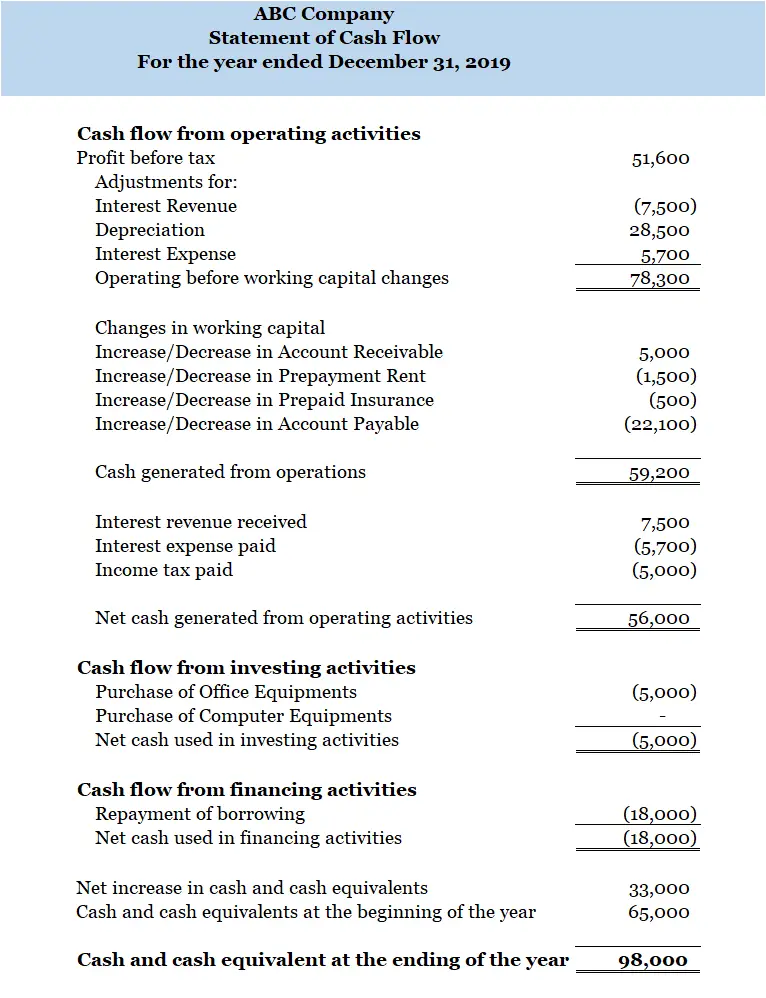
In accordance with IAS 1, the presentation of financial statements of an entity shall consists of financial information that enable the reader to clearly identify such information together with the disclosure notes. Furthermore, each each financial statement, the following information shall be presented:
- The name of the entity being reported as well as other mean of identification.
- Clearly show that the financial statement are for group of entities or for any individual entity. For group, we normally call consolidated financial statements.
- Shall clearly show the period or date being reported in all set of financial statements including the disclosure notes.
- Shall clearly indicate the presentation currency; especially if functional currency is difference from presentation currency.
- The entity shall also clearly mention the level of rounding used in presenting amounts in the financial statements.
What are the complete set of financial statements?
In addition, according to IAS 1, each entity shall prepare a complete set of financial statements which consist of the following:
- Statement of financial position or Balance Sheet as at the end of the reporting period;
- The Income Statement or Statement of profit or loss and other comprehensive income for the reporting period;
- The statement of changes in equity for the reporting period;
- Cash flow statement for the reporting period;
- Disclosure notes including the summary of significant accounting policies and any other explanatory information;
- Each entity shall prepare its financial statements to include the comparative information for the preceding period as well as in the disclosure notes;
- If any entities apply any accounting policies retrospectively or make any retrospective restatements of any items in the financial statements, such entity shall prepare financial statements including the beginning of the preceding period.

Comments are closed.