Present value (PV) of an ordinary annuity is a measure of how much value of money now for periodic equal future cash flows at a given interest rate and timeframe.
In this article, we cover the definition of the present value of an ordinary annuity, how to calculate it by using different methods as well as how to generate the present value of an ordinary annuity table.
So let’s dive in!
What is Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity?
Before understanding the present value of an ordinary annuity, let’s understand two key concepts; present value and ordinary annuity.
Present value refers to the inverse of future value. It is the measurement of the current value of a future cash flow.
An ordinary annuity is an annuity in which the cash flows, either cash inflows or cash outflows, occur at the end of each period.
Thus, the present value of an ordinary annuity is the measurement of the current value of future periodic equal cash flows that occurs at the end of each period.
How to Calculate the Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity?
In order to calculate the present value of an ordinary annuity, we can use different methods. In this article, we take only three methods to illustrate. These are the long method, the short method as well as Excel Spreadsheet method.
The long method involves the calculation of the present value of each future cash flow at each individual discount factor or present value interest factor and summing up together. In this method, the present value interest factors are taken from the present value interest factors table.
For this method, we commonly a table in order to calculate the present value of an ordinary annuity. The PV interest factors (PVIF) can also be calculated by using the below formula:
PVIF (i, n) = (1+i)-n
Therefore, the PV of an ordinary annuity is as follows:
PV of an ordinary annuity = C1 × (1+i)-1 + C2 × (1+i)-2 + C3 × (1+i)-3 +……. + Cn × (1+i)-n
Where:
C = Each cash flow
i = Interest
n = Period
On the other hand, in the short method of calculating the PV of an ordinary annuity, we simply taking the annuity cash flow to multiply directly with the PVIFA of an ordinary annuity.
The PVIFA of an ordinary annuity here is different from normal PVIF or discount factors. The PVIFA of an ordinary annuity are calculated as follows:
PVIFA (i, n) = [1 – (1+i)-n]/i
Hence, the PV of an ordinary annuity = PMT × PVIFA (i, n)
Where:
PMT = Annuity cash flow
PVIFA (i, n) can be calculated from the above formula or taken from the present value of an ordinary annuity table.
The last method of calculating this is by using the Excel Spreadsheet. We will produce an Excel Spreadsheet to illustrate the calculation in the later section below.
Example
Assume that ABC Co wants to assess how much it should pay in order to purchase a particular ordinary annuity. The cash flow of the annuity is $500 at the end of each year for 5 years. This ordinary annuity has a minimum return of 7%.
Calculate the PV of an ordinary annuity above by using the three methods above.
1. PV of an Ordinary Annuity under Long Method
Under the long method, we need to look at the present value interest factors table or using the formula above to calculate the PV interest factors. We can calculate as per the table below:
| Year (n) | Cash Flow [A] | PVIF at 7% [B] | Present Value [C = A × B] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 500 | 0.935 | 467.29 |
| 2 | 500 | 0.873 | 436.72 |
| 3 | 500 | 0.816 | 408.15 |
| 4 | 500 | 0.763 | 381.45 |
| 5 | 500 | 0.713 | 356.49 |
| PV of annuity | 2,050.10 |
Hence, the PV of an ordinary annuity is $2,050.10.
2. PV of an Ordinary Annuity under the Short Method
Under the short method, we just need to calculate the PVIFA of an ordinary annuity as per the formula above or simply look at the PV of an ordinary annuity table. In this example, we will use the PV of an ordinary annuity table. So, we can calculate the PV of an ordinary annuity as follows:
PV of an ordinary annuity = PMT × PVIFA (i, n)
Where:
PMT = $500
PVIFA (7%, 5yrs) = 4.100 (From PV of an ordinary table)
Hence, PV of an ordinary annuity = 500 × 4.100 = $2,050
3. PV of an Ordinary Annuity by Using Excel Spreadsheet
By using the Excel Spreadsheet, we can calculate the present value of an ordinary annuity as follows:
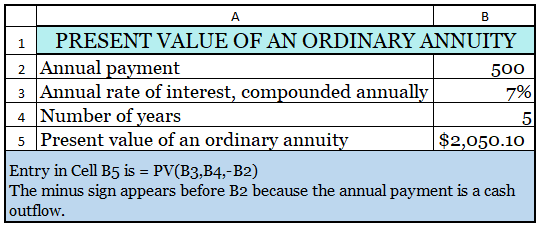
You can follow the illustration as per the calculation above to develop your own Excel spreadsheet calculation.
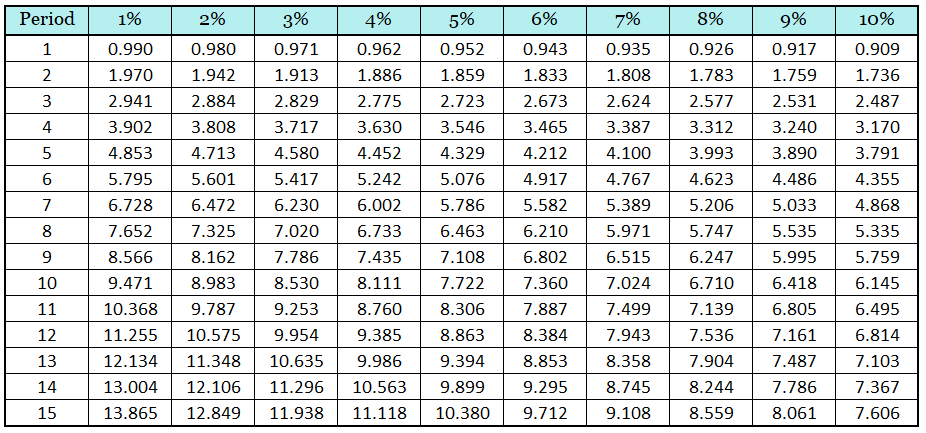
Present Value of an Ordinary Annuity Table
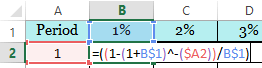
The present value of an ordinary annuity table is a table of PVIFA of an ordinary annuity that we take in order to calculate the PV of an ordinary annuity.
We can generate this table by using the PV interest factors of an ordinary annuity formula below:
PVIFA (i, n) = [1 – (1+i)-n]/i
Thus, by using the above formula, we get the PV of an ordinary annuity table below:
Conclusion
To sum up, the present value of an ordinary annuity is very usual to know how much is the current value of future cash flow to be received at a given interest rate. It can be calculated in different ways; by using the long or short method as well as Excel Spreadsheets.
