Introduction
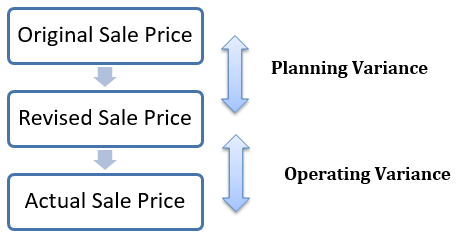
Sales price variances can occur both in planning and operational forms. The sales price planning variance is often caused due to uncontrollable or external market factors, while Sales Price Operational Variance occur internally. So what is Sales Price Operational Variance?
Definition
Sales price operational variance can be defined as:
“The difference between product units sold at actual selling price and the revised selling price”
The correlation between operating and planning variances can be described as:
Sales Price Operational Variance Formula
Sales price Operational variance or sometimes called Sales Price Operating Variance can be calculated for a difference in the revised sales price and actual sales price as:

Working Example
Suppose Techno Blue sells 3 products P1, P2 and P3 with the following data:
| Product | Actual Sale Price $ | Revised Sales Price $ | Budget Sale Units | Actual Sales Units |
| P1 | 18 | 20 | 2000 | 1900 |
| P2 | 25 | 30 | 2000 | 2300 |
| P3 | 25 | 22 | 2000 | 2000 |
There can be several reasons both internal and external causing a change in the sales price discussed in detail below. The total sales price planning variance for 03 products can be calculated as:
| Product | (Revised Sales Price – Actual Sales Price) × Actual Units Sold | Variance in $ | Favorable/Adverse |
| P1 | (20 – 18) × 1900 | 3,800 | Adverse |
| P2 | (30 – 25 ) × 2300 | 11,500 | Adverse |
| P3 | (22-25) × 2000 | 6,000 | Favorable |
| Total Sales Price Planning Variance | $ 9,300 | ADVERSE |
Interpretation and Analysis
The management plans for budgets and estimates at the beginning of the year, several factors cause a change in the selling prices. The management then revises the original budgeted sale prices. Achieving the revised sales price is the responsibility of the operational managers, however, some controllable or unforeseen factors can still cause the difference in the actual sale prices. The deviation in the revised sales price and the actual sales price is operational sales price variance. Some external factors, such as new entrants in the market can compel the management to sell the products at lower than revised prices. Some operational inefficiency such as unavailability of important raw material components can cause an increase the production costs. Several factors contribute to budget revisions and sales price operational variances:
- The threat of new competitors compelling management to lower the sales prices
- Unavailability of input components or increase in the raw material prices
- Inefficiency in operations leading to wastes and idle labor hours
- Seasonal product demand or lack of competition may temp the management to increase sales prices
- Operational efficiencies and economies of scale can also lead to favorable sales price variances
Once the management revises the original sales prices, it becomes the core responsibility of the operational managers to achieve those results. Sales price operational variances often occur due to controllable actions.
Importance of Sales Price Operational Variance
Uniform and bulk productions keep the operating costs at consistent levels; hence deviations in the costs are at a minimum. For manufacturing facilities producing customized and large products, the costs may vary significantly with each product batch or model. External market factors change dynamically, which requires quick response and adjustments in planning and budgets.
Closing the gap between revised and actual sales price can be achieved with prompt responses. Continuous process improvement and robust planning can help achieve lower than budget product costs. It also helps management to understand the real causes of the revised sales prices and actual sale price difference. Even after revising sales prices, after the product launch, the marketing department may suggest changing the sales prices. It is important for management to analyze such factors and plan for future to create favorable sales price variances.
Advantages of Sales Price Operational Variance
Sales price operational variance offers helpful insights to the management. Some of the advantages include:
- It helps management to act accordingly to market competition
- Bridging gaps between revised and actuals sales prices require considerable operational improvements
- It increases staff motivation to achieve operational efficiencies
- Management can discover the coordination gaps between marketing and operational managers’ plans
Limitations of Sales Price Operational Variance
As in any control measure, the sales price operating variance also has some limitations:
- It may cause a conflict of planning among the marketing and operational managers, as marketing department will be more concerned with external competitors analysis
- Failing to achieve revised budgets and reporting further sales operating variances may discourage the operational managers
- Few external factors such as sales price competition cannot be controlled by the operational managers
- Industry standards may be difficult to analyze or even with the availability of information may become difficult to meet the industry standards
Conclusion
Revising the sales price budgets is inevitable for any management; however, closing the revised and actual sale price gaps should be the real focus. A careful interpretation of the drivers behind the variances can help achieve the desired goals. Sales price largely depend on the input components, securing long term supplier contracts, bulk buying discounts, and regular supplies can help reduce costs. Efficient operations and labor can also contribute towards lower product costs that can help achieving favorable sales price variance. In a larger context, the sales price operating variance should be seen in conjunction w
