A stakeholder is an entity that has an interest in a company’s operations. Stakeholders can be internal or external. Usually, these entities make decisions regarding their relationship with a company based on the financial statements. These statements include a proper presentation of a company’s financial records in accordance with applicable standards.
For stakeholders to make well-informed decisions, companies must present true and fair information on their financial statements. However, establishing whether the financial statements are accurate may be a challenge. Therefore, companies will use the services of an independent auditor. Auditors are third parties who report on a company’s financial statements based on their findings. If auditors find issues with those statements, they will issue a qualified audit report.
What is a Qualified Audit Report?
A qualified audit report is a type of audit report issued by an auditor that contains a qualified opinion. This report is a type of modified report that alters the unqualified opinion provided by auditors. There are several reasons why a company may issue a qualified audit report. For auditors to issue a qualified audit report, a company’s financial statements must not meet the definition of an unqualified opinion.
Primarily, auditors issue this audit report when a company’s financial statements have material misstatements. However, these material misstatements must not be pervasive or else it would require an adverse opinion. Pervasive is a term in auditing that describes whether misstatements affect the financial statements as a whole.
A qualified audit report may also come due to the audit evidence that auditors obtain. If auditors cannot collect audit evidence that is sufficient and appropriate, they will use a qualified audit report. Similar to the above scenario, the effects of these issues must not be pervasive. Otherwise, auditors have to issue a disclaimer of the opinion audit report.
Overall, this audit report only focuses on areas that are not pervasive but material. When auditors report these issues, they use “except for” to exclude the rest of the financial statements. Instead, they specify the specific areas that cause the audit report to get qualified. Similarly, auditors will provide a basis for qualified opinions in the audit report to explain their opinion.
What does the Qualified Audit Report mean?
This audit report questions a specific part of the financial statements. As mentioned, it may include a material misstatement or not have sufficient appropriate audit evidence. It sends a negative signal to the stakeholders. However, it is not as serious as the other qualified opinions, the adverse opinion, and the disclaimer of opinion. The primary difference between both is the pervasiveness of the issues.
The qualified audit opinion also doesn’t provide the same level of positive assurance as to the unqualified audit opinion. However, it also doesn’t instill confidence in stakeholders like the unqualified opinion. As stated, there are several reasons why the auditors may qualify their audit opinion and report. However, they usually mention those areas and exclude the rest of the financial statements from them.
Overall, the qualified audit report questions a company’s financial statements. However, it does not impact all areas. As mentioned, this report only specifies an item or area that does not satisfy the conditions for an unqualified audit report. While it is a qualified opinion, the interpretation depends on how stakeholders perceive the audit report.
When do auditors issue the Qualified Audit Report?
Generally, auditors issue this audit report when a financial statement item has issues. As mentioned, these usually include material misstatements and sufficient appropriate audit evidence being unavailable. However, the effects of these issues must not be pervasive or else it will warrant a different qualified opinion.
ISA 705 (Revised) Modifications to the Opinion in the Independent Auditor’s Report deals with the qualified audit report. The standard specifies the circumstances when auditors need to modify their audit opinion. ISA 705 (Revised) states that auditors must amend their opinion in the auditor’s report when one of the following conditions exists.
- Based on the audit evidence obtained, the financial statements as a whole are not free from material misstatements.
- The auditor cannot obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence to conclude that the financial statements are free from material misstatement as a whole.
Furthermore, ISA 705 (Revised) states that auditors should express a qualified opinion when one of the following conditions exists.
- After obtaining sufficient appropriate audit evidence, the auditor concludes that misstatements exist in the financial statements. These misstatements may exist individually or in aggregate and are material.
- The auditor cannot obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence on which to base an opinion. However, the auditor concludes that the possible effects on the financial misstatements could be material but not pervasive.
How does the Qualified Audit Report differ from other reports?
The qualified audit report modifies the standard unqualified audit report. Therefore, it falls under the modified audit reports category. There are several areas where this report changes. ISA 705 (Revised) guides auditors on altering the audit report when issuing a qualified audit report. The primary difference is the “except for” term used to exclude the financial statements from the issues.
Apart from the primary difference, this audit report also affects the basis for the opinion paragraph. When presenting a qualified audit opinion, auditors must alter this paragraph to the basis for a qualified opinion. This section must also include reference to the framework on which the auditors report. The paragraph will also differ when the qualified opinion is for material misstatements or the unavailability of sufficient appropriate audit evidence.
Example
As mentioned, the qualified audit report affects two primary areas in the audit report. These include the opinion section, which becomes the Qualified Opinion paragraph. Similarly, it consists of the basis for the opinion section, which becomes the Basis for Qualified Opinion paragraph. A sample opinion paragraph from a qualified audit opinion may look like the following.

The above is a qualified opinion paragraph for the financial statements, including material misstatements. A sample opinion paragraph for when auditors cannot obtain sufficient appropriate audit evidence regarding material areas may look as follows.
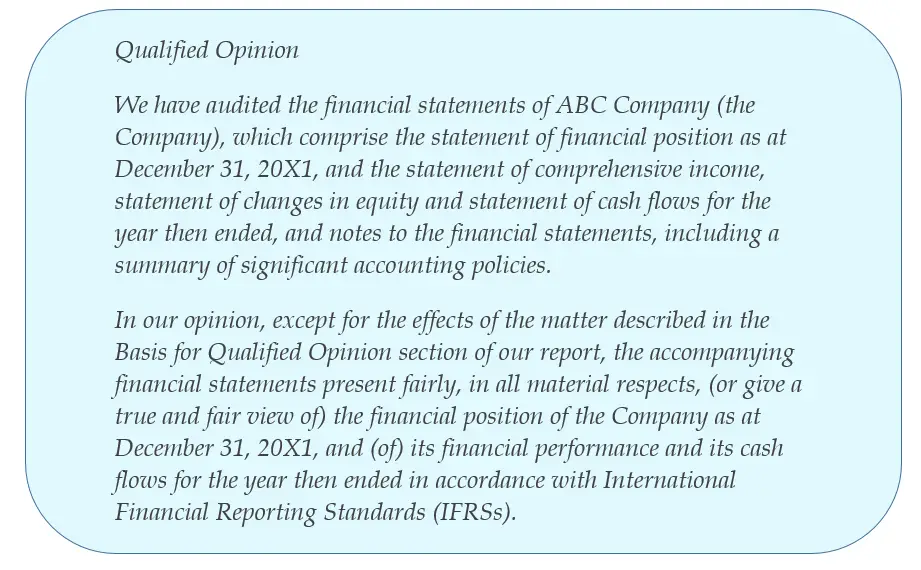
Both of these excerpts are from the International Standards on Auditing, ISA 705 (Revised). Both of these will include details in the Basis for Qualified Opinion paragraphs.
Conclusion
A qualified audit report is a type of audit report that auditors issue with a qualified opinion. There are two reasons why auditors will issue this audit report. These include material misstatements in the financial statements and unavailability of sufficient appropriate audit evidence. However, the effects of these should not be pervasive.
Reference
- ISA 705 (Revised) Modifications to the Opinion in the Independent Auditor’s Report [Source]
