Inventory represents any goods or stock that companies sell or produce. Usually, inventories go through a conversion process before coming to their finished form. In some cases, however, companies may sell products as acquired from suppliers. Either way, inventories represent the primary income source for companies that deal in physical stock.
Inventories are a part of a company’s assets. Usually, these comprise current assets, which are short-term. Similarly, inventories constitute a part of a company’s working capital. Working capital basically refers to the difference between the current assets and liabilities of a company. For most companies, a proper system of working capital management is crucial for long-term success. Since inventories are a part of working capital, inventory management is also critical for companies.
What is Inventory Management?
Inventory management is a process that companies use to handle the storage and ordering process for stock. This process starts when companies acquire raw materials and lasts until these materials get converted to finished goods. From the initial acquisition of inventory to the ultimate disposal, inventory management plays a crucial role.
Companies may use various strategies to manage their inventories properly. These may include using inventory management methods such as just-in-time, material requirement planning, economic order quantity, etc. The purpose of both of these is to balance the risk of shortages with inventories.
Companies can avoid shortages by keeping the maximum amount of inventory on hand all the time. However, the answer isn’t as simple as that. Companies also need to bear costs related to handling the stock and storing it, which may be significant in some cases. Companies will always want to decrease or minimize these expenses.
On the other hand, companies can also order inventory whenever needed without holding any stock. That is how a just-in-time system works. However, companies also bear costs related to ordering, for example, transportation costs. Therefore, it may also increase a company’s costs related to inventory.
What is Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)?
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) represents the ideal order quantity that companies need to order every time. The idea behind EOQ is to minimize handling and order costs for companies. However, it doesn’t focus on costs only. It also considers the demand for products and ensures that companies don’t face any inventory shortage.
The economic order quantity model, developed in 1913 by Ford Harris, focuses on two types of costs, as stated above. Firstly, it considers ordering costs for companies. Typically, ordering costs are lower when companies maximize the quantity ordered for every batch of orders. This way, companies can achieve economies of scale and minimize the per-unit cost of inventory.
On the other hand, handling costs related to storing inventory. Companies can keep these costs down by holding the least amount of inventory. It is because more stock requires more time to sell. Therefore, the longer it takes for companies to sell their stock, the more storage costs they will incur. Hence, ordering and handling costs go against each other.
The economic order quantity model solves that problem by establishing an ideal inventory point. It shows how much inventory a company should order each time to balance ordering and handling costs. Similarly, it considers the demand for a company’s products. This way, it ensures that a company does not face any inventory shortages.
How to Calculate the Economic Order Quantity?
The economic order quantity model formula considers the demand for inventory and the total cost of ordering and handling it. By considering all of these, EOQ provides an ideal point at which these costs will be the lowest while also avoiding inventory shortages. The EOQ formula is as below.
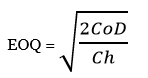
In the above formula, ‘D’ represents the annual demand for products. ‘Co’ shows the ordering costs for products. Lastly, ‘Ch’ denotes the handling costs or storage cost per unit of products.
Example
A company, Bright Co., wants to establish an ideal inventory point to minimize costs and chances of stockouts. The company estimates an annual demand of 25,000 units per annum. Similarly, Bright Co. estimates its ordering costs to be $80 per order. Lastly, the company believes its storage cost per unit will be $25 per unit.
From the example above, we have the following information:
D = $25,000
Co = $80 per order
Ch = $25 per unit
Therefore, Bright Co.’s economic order quantity will be as follows.
Economic Order Quantity = √(2 x 25,000 units x $80 per order / $25 per unit)
Economic Order Quantity = √160,000 = 400 units
What is the Importance of Economic Order Quantity?
Economic order quantity is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it focuses on minimizing inventory costs for companies. It is a critical part of inventory management from which companies can benefit. Similarly, it considers the demand for products, which can play a substantial role in avoiding stockouts. It can further increase profitability.
Economic order quantity can also be useful when companies have multiple products. Usually, it is easier to handle single products. When it comes to multiple items, it can be challenging to track them and keep tabs on them. Therefore, EOQ can play a significant role in solving the challenges that come with various products.
Conclusion
Inventory management is a crucial part of a company’s working capital management. It involves reducing inventory-related costs and minimizing stockout chances. One model that companies can use to do so is the Economic Order Quantity. The EOQ model helps companies calculate the ideal order quantity that can achieve that purpose.
